Comparing Carnivore Diet vs Keto: Which is The Better Low Carb Diet For Your Needs
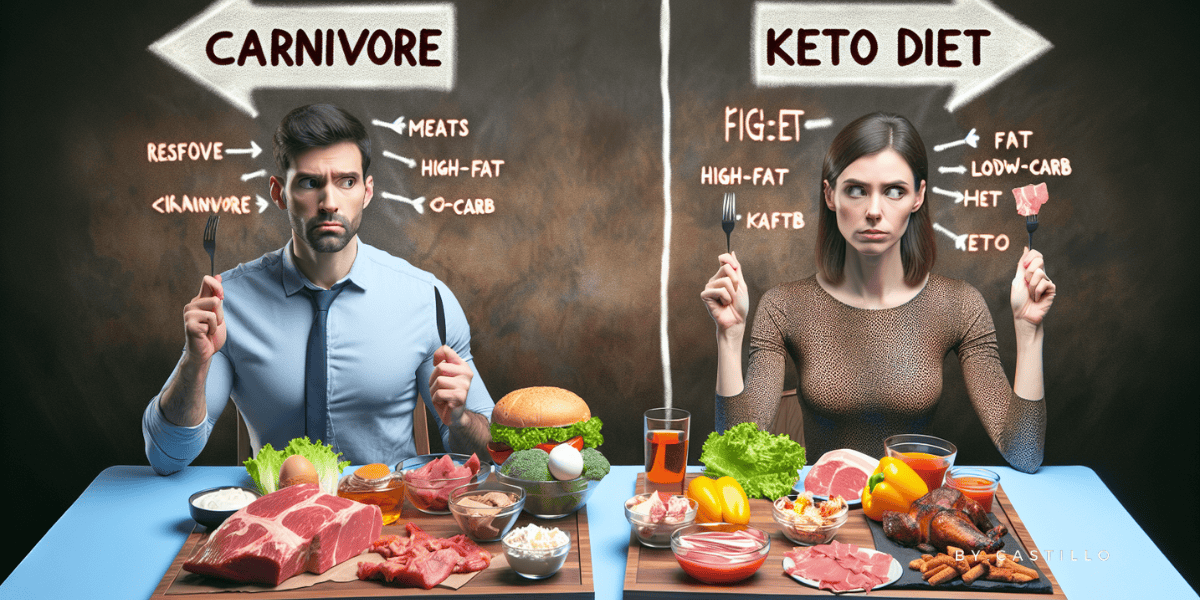
Starting a low-carb journey? The carnivore diet and the ketogenic diet both slash carbs, yet they take unique paths when it comes to fats and proteins. Let’s dive into ‘carnivore diet vs keto’ to slice through the haze of confusion and uncover which path may be the perfect fit for your health adventure.
Key Takeaways
The Carnivore diet is a zero-carb, animal-based eating plan, hypothesized to align with our evolutionary biology and potentially act as an elimination diet to identify food sensitivities, though it risks nutritional deficiencies due to lack of plant-derived nutrients.
The Keto diet is a low-carb, high-fat regimen designed to induce ketosis for weight loss and improved metabolic health, offering variations like the Cyclical Ketogenic Diet (CKD) and Targeted Ketogenic Diet (TKD) to cater to different lifestyles.
Both Carnivore and Keto diets minimize carbohydrate intake and can pose long-term sustainability challenges due to their restrictive nature, requiring careful consideration of lifestyle, goals, and potential health implications for proper adherence.
Exploring the Carnivore Diet: A Zero-Carb Approach to Nutrition
The Carnivore diet, a unique regimen, consists solely of animal-based foods, which means followers of this diet eat animal products exclusively.
People following the carnivore diet eat meat as their primary food source, emphasizing the simplicity and straightforwardness of the diet, focusing on eating meat when hungry and until full without the need to count macronutrients or analyze carb content.
This dietary approach eliminates all plant-based foods and aims to minimize carbohydrate intake to virtually zero. It’s built around dietary fat and proteins, including saturated fats and essential amino acids, all derived from animal sources like:
beef 🥩
pork 🍖
chicken🍗
fish 🐟
wild game 🦌
While there are various carnivore diets, they all share the same foundation of excluding plant-based foods
But what’s the rationale behind it?
The Premise Behind the Carnivore Diet
The Carnivore diet is based on the hypothesis that early humans thrived on a carnivorous diet, suggesting that our digestive system may be best suited for animal proteins and fats.
Proponents argue that consuming only animal products allows us to optimize our health by aligning with our evolutionary biology. But it’s not just about reverting to our primal eating habits.
The Carnivore diet can also serve as an elimination diet, helping individuals determine personal food sensitivities.
Potential Benefits of Embracing an All-Meat Diet
The Carnivore diet offers several benefits, including:
Controlling appetite and aiding in weight loss due to its high-protein and low-carb nature
Increasing metabolic rate
Better blood sugar control due to the absence of plant-based carbohydrates
Some individuals have even reported relief from autoimmune diseases and gastrointestinal disorders like irritable bowel syndrome, experiencing health benefits.
Understanding the Ketogenic Diet: A High-Fat, Low-Carb Regimen

Now, let’s shift our focus to the Ketogenic or Keto diet.
This low-carb, high-fat diet aims to induce a metabolic state called ketosis, where fat becomes the primary fuel source. It prioritizes foods like grass-fed beef, wild-caught meat, fish, seafood, and organic vegetables, while severely limiting carb-rich foods such as breads, cereals, pasta, rice, and sugary fruits.
What implications does this have for your body and health?
How Keto Promotes Fat Burning and Weight Loss
Inducing a metabolic state known as ketosis, the Keto diet reduces carb intake, paving the way for fat to be the primary energy source.
This shift in metabolism, coupled with a high-fat content and moderate protein intake, reduces lipogenesis (fat storage) and may increase the amount of fat burned at rest and during physical activities.
All this facilitates the process to lose weight by preserving muscle mass while promoting burning fat and reducing appetite and food intake.
Varieties Within Keto Diets
Like the keto and carnivore diets, the Carnivore diet and the Keto diet too offer variations tailored to specific needs and preferences.
The Cyclical Ketogenic Diet (CKD) incorporates periods of higher carb intake between standard keto dieting phases, while the Targeted Ketogenic Diet (TKD) allows additional carb consumption based on workout routines, supporting energy levels during exercise.
Direct Comparison: Carnivore vs Keto Diets

Having individually explored each diet, it’s time to compare them directly. Both the Carnivore and Keto diets aim to reduce carbohydrate consumption, shifting the body’s fuel source from glucose to fat. But while they share this common goal, they differ in their allowed foods and level of planning involved.
This brings up the question:
How do these variances affect the macronutrient breakdown and food choices in each diet?
Macronutrient Breakdown and Food Choices
The Carnivore diet does not adhere to specific macronutrient breakdowns, unlike the Keto diet which has concrete daily macronutrient intake goals.
The Keto diet permits a range of diverse food items, including:
fruits🍊
vegetables🥦
nuts 🥜
seeds🌻
These food groups are excluded in the Carnivore diet.
Therefore, while ketogenic dieters need to balance fat and protein to maintain energy and satiety, meal planning in the Carnivore diet is simpler, with less focus on macronutrient ratios, as most food groups are not included.
Health Implications and Nutrient Profiles
When it comes to health implications and nutrient profiles, both diets raise concerns.
The Carnivore diet is associated with increased risks of nutritional deficiencies due to its exclusion of important food groups that provide essential nutrients.
On the other hand, long-term adherence to the Keto diet may lead to nutrient deficiencies, particularly in fiber, which may affect the diet’s long-term sustainability.

Evaluating Dietary Sustainability: Can You Stick to It Long-Term?
Discussing dietary sustainability next, the stringent nature of both diets could pose challenges to long-term adherence.
For the Keto diet, maintaining a limit of 20 to 25 grams of net carbohydrates per day can be difficult to sustain in the long run.
Meanwhile, the Carnivore diet’s total elimination of plant-based foods raises questions about its long-term healthiness.
The Challenge of Restrictive Eating Habits
The Carnivore and Keto diets both pose challenges due to their restrictive eating patterns.
Switching from a strict Keto phase to a more relaxed form can result in weight regain and impact long-term health due to the yo-yo pattern of weight loss and regain.
For the Carnivore diet, the exclusion of all plant foods should be done for limited periods and under close supervision due to potential imbalances.
Incorporating Variety and Balance
Although restrictive, the Keto diet allows for a more flexible approach to meal planning, making it easier to meet daily nutrient requirements through a range of food choices.
Transitioning to a less restrictive phase following a Keto diet can help individuals incorporate a wider variety of foods and ensure balanced nutrition.
Tailoring Your Diet: Which One Aligns With Your Lifestyle?
So, which diet suits you better? Carnivore or Keto?
The answer largely depends on your lifestyle, goals, and preferences.
Some individuals find the zero carb diet, also known as the Carnivore diet, easier to adhere to, as it does not require counting macronutrients or monitoring carb intake.
For the Active Individual: Energy and Performance Considerations
For those leading an active lifestyle, considerations of energy and performance become critical.
Both diets require adaptation to alternative energy sources.
While Keto diet followers experience more readily available energy in ketosis, those on the Carnivore diet may need to adapt to an alternative energy source due to the lack of carbohydrates.
Some athletes on the Keto diet have even experienced a decrease in performance, especially during high-intensity activities that traditionally rely on carbohydrates for energy. This is why the Cyclical Keto Diet and Targeted Keto Diet are popular among active individuals.
Managing Health Conditions: Autoimmune Diseases and Blood Sugar Control

Managing health conditions such as autoimmune diseases and blood sugar control can also influence your choice of a healthier diet, steering away from processed foods.
The Keto diet has shown potential benefits for diabetes management, with research demonstrating improved glucoregulatory control in diabetics, reducing the need for anti-diabetic medications.
Transitioning to a Low-Carb Diet: Tips and Strategies

Considering the switch?
Transitioning to a low-carb diet calls for adequate preparation, mental preparedness, and strategies to tackle social situations and dining out.
It’s not always a smooth ride, though.
Some people experience flu-like symptoms, often referred to as the ‘keto flu’, when transitioning to a low-carb diet.
How to Avoid The Keto Flu/Low-Carb Diet Symptoms
You will most likely experience these symptoms when starting your low-carb diet. Some people start experiencing these symptoms within a few days of transitioning to the keto diet plan or the carnivore diet plan.
Keto Flu/Low Carb Diet Symptoms:
Headache
Fatigue
Dizziness
Nausea
Irritability
Difficulty sleeping
Muscle cramps or soreness
Sugar cravings
Brain fog or difficulty concentrating
Constipation or diarrhea
Increased hunger
Decreased exercise performance

These symptoms can often be avoided by taking supplements to help combat the side effects of low-carb diets. Grab a bottle of BHB Salts, Pidialyte, or Keto Cycle Fuel Powder that are filled with electrolytes to combat these symptoms.
Don’t worry! These symptoms are only temporary and go away once your body has adapted to a low-carb diet.
Starting Your Diet Right: First Steps and Preparing Mentally
It’s vital to kick off your diet on the right note.
Always consult with a healthcare professional to ensure the diet aligns with your fitness goals and activity levels.
Resources such as carnivore diet tips and a carnivore diet snack list can aid in a more successful transition to the Carnivore diet.
The same goes for the keto diet, find helpful keto tips online to help you get off to a strong start!
Ease Your Way Into The Diet
If you decide to start the keto or carnivore diet, make sure you ease your way into the diet by slowly depleting your carb intake.
Doing this will help you avoid or minimize the effects of the keto flu/low-carb diet symptoms and help you stay consistent when starting.
Navigating Social Situations and Dining Out
When dining out or attending social events, adhering to the Carnivore or Keto diet necessitates mindful food choices to stay within dietary limits.
Carrying electrolyte supplements or other supportive measures may be necessary to adhere to your diet when eating out.
Carnivore Diet vs Keto Summary
So, there you have it.
The Carnivore and Keto diets are both low-carb approaches with their own unique features, benefits, and challenges.
The Carnivore diet simplifies meal planning by focusing solely on animal-based foods, while the Keto diet offers more variety and requires careful macronutrient tracking.
Both diets have potential health benefits, but also raise concerns about long-term sustainability and nutrient deficiencies.
FAQs
What are the main differences between the Carnivore and Keto diets?
The main difference between the Carnivore and Keto diets is that the Carnivore diet only includes animal-based foods with virtually no carbs, while the Keto diet allows for a limited intake of carbohydrates and includes a variety of foods.
Are there any potential health benefits associated with these diets?
Both the Carnivore and Keto diets have potential health benefits, such as weight loss and improvements in blood sugar control, diabetes management, autoimmune diseases, and gastrointestinal disorders. These diets offer a range of potential health advantages.
How can I transition to a low-carb diet?
To transition to a low-carb diet, consult with a healthcare professional to align with your fitness goals, prepare mentally for the change, and develop strategies for navigating social situations.
What are some challenges of these diets?
Both diets pose challenges due to their restrictiveness and potential for nutrient deficiencies, making long-term adherence difficult and raising concerns about overall nutrition.
Can active individuals follow these diets?
Active individuals can follow these diets, but they need to consider energy and performance factors. Both diets require adaptation to alternative energy sources, and high-intensity activities may lead to decreased performance for athletes on the Keto diet.






